Middle Eastern flag colors represent a shared sense of identity among all Arab countries. This concept comes from Pan-Arabism, which grew in popularity in the region during the 19th and 20th centuries. Pan-Arabism is the the notion or advocacy of all Arab states forming a political alliance or union and was based on the belief that Arabs should unite to form a single nation with shared political, cultural, and religious interests, thus fostering and spreading the significance of the Arabic language, as well as their resistance to Western influences in the region.
We can learn about a country’s history by looking at its flag, because flags typically depict what a state’s founder provided for its citizens. Furthermore, flag designs typically express the nation’s actual identity as well as the values upon which the nation was created, making it important to comprehend the significance of each flag.
1) Saudi Arabia

- The “Shehada,” or statement of faith in Islam, is depicted on this flag.
- The color green represents Islam.
- The sword depicts the country’s application of justice.
- The flag was adopted on March 15, 1973.
2) Egypt
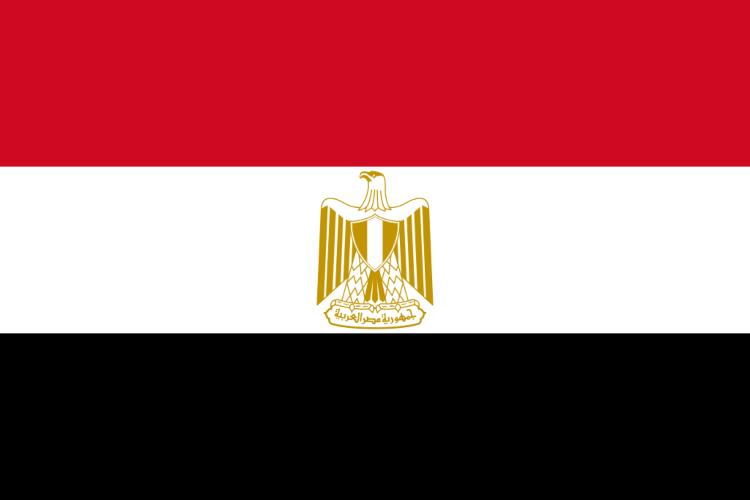

- The martyrs’ sacrifices and blood are commemorated by the color red.
- The white symbolizes peace and the black represents the dark period of occupation.
- The eagle is a symbol of power and strength.
- The flag was adopted on October 4, 1984.
3) Lebanon

- The two red stripes on the flag signify Lebanese bloodshed in order to defend the country against invaders, while the white color represents snow as a symbol of purity and peace.
- The cedar tree, positioned in the middle of the flag, is inspired by the mountains of Lebanon and is considered the symbol for Maronite Christians.
- The flag was adopted on December 7, 1943.
4) Yemen
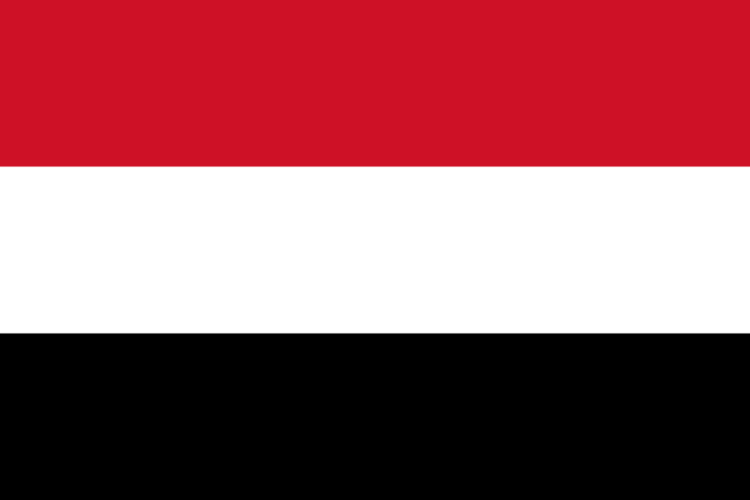

- The Yemeni flag was adopted during the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, during which Arab nationalism was a major theme within the region.
- The black color depicts the civil war between the north and the south, while the white represents a bright future, and the red color stands for the scuffle to achieve independence and unity.
- The flag was adopted on May 22, 1990.
5) Palestine

- The black represents the suffering and persecution of the Palestinian people, the white represents the peace and love, as well as purity behind all the messages of the prophets that have been sent to Palestine’s sacred land, and green symbolizes hope for a better future and blessings.
- The flag was adopted on November 15, 1988.
6) Algeria

- The green color in the Algerian Flag represents Islam and the white represents peace and purity.
- The red color represents the blood of martyrs during the Algerian War of Independence that took between 1954 and 1962, and the star and crescent are also symbols of Islam.
- The flag was adopted on July 3, 1962.
7) Morocco

- The color red represents valor and bravery and green represents Islam. Also, each of the five straight lines in the green pentagram signifies one of the five pillars of Islam.
- The flag was adopted on November 17, 1915.
8) United Arab Emirates

- The color red in the UAE flag represents bravery, strength, and together in unity.
- The color green represents hope, joy, optimism and love, as well as the prosperity of the nation.
- Black represents the defeat of enemies and mental strength.
- White represents peace and honesty.
- The flag was adopted on December 2, 1971.
9) Syria
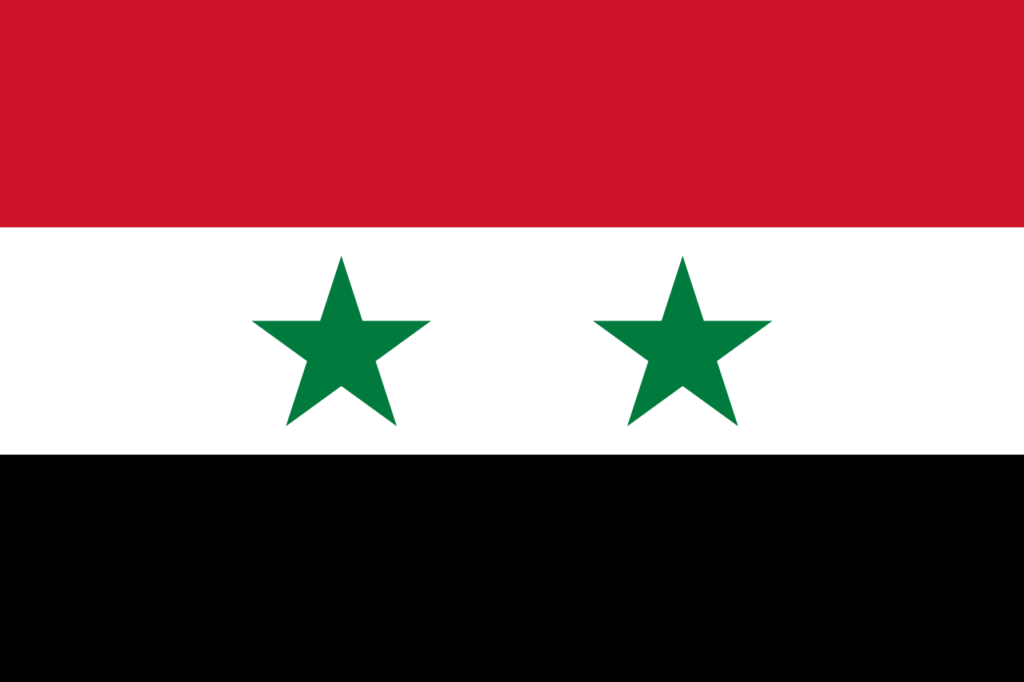

- The flag of Syria was previously changed to show the country’s commitment to Arab unity.
- The flag is based on the Arab Liberation Flag that represents four major dynasties of Arab history.
- Black represents the Abbasid Dynasty.
- Green represents the Fatimid Dynasty.
- White represents Umayyad Dynasty.
- Red represents Hashemite Dynasty.
- Originally adopted in 1958, the current flag of Syria has been in use since 1980.
10) Iraq

- Red represents the courage and struggles of Iraq.
- Black represents oppression and Islam’s triumph in the nation.
- White represents the generosity of the Iraqi people.
- The flag was adopted on July 31, 1963.
Arab flags share comparable themes, such as religion, Pan-Arabism, and martyrdom from battles in the pas, and common colors also emphasize the sense of unity that existed and continues to exist today. However, each flag has a distinct identity that highlights the nation’s past experiences.