Fake news isn’t a new phenomenon. It’s been used for as long as we can remember and way before that as well. Difference is, in the digitalized world of today and with our usage and reliance on social media, bogus stories have the capacity to spread like wildfire at un precedented rate, sucking each and every person into a vortex of lies and deceit. Fortunately, there are warriors out there who offer us advice as to how we can spot this pandemic of fake news, and what to do about it.
Use your analytical mindset
One of the main reasons fake news is an issue is due to its believablity, making it that much easier to become a viral spiral. Keep in mind as well that fake news is also written in order to produce “shock value.” In other words, a strong instinctive reaction such as fear, rage or anger. Having said that, it is essential that you keep your emotional response to such stories in check. Approach what you see and hear rationally and critically in order not to fall into the vortex of deceit.
Are you getting all sides of the story here?
Usually, a news article would offer various viewpoints for the case at hand, rather than stemming from just one side and angle. Of course for many, these types of news fit their narrative like a perfect piece to the puzzle of their resentment and world views, further molding their perspective on what they already believe and/or which way they’re already leaning towards. If the angle of the story is strictly one-sided, then it’s safe to assume you’re not getting the full story here.
Check the source(s)
If you happen to come across any story from what may seem at first to be a credible source of some sort, but haven’t actually heard of before, then it’s time to do some digging. How? Check the web address for the page you’re reading. Look for spelling errors in company names, or strange-sounding extensions such as “.infonet” and “.offer,” as opposed to “.com” or “.co.uk.” These may potentially suggest that the source is suspicious.
Check the About Us section
Check the “About Us” section on a website, which may be placed either somewhere on top or on the bottom of the site. This section usually details the purpose of the website, and you can find out whether or not they have a team of journalists and writers, as well as if they offer guest writers to contribute to the platform. If this section lacks information regarding their location, their purpose and their staff, it’s worth reconsidering the credibility of their articles/posts.
Who else is reporting the story?
Some questions to ask after reading a rather bold headline or story are: has anyone else picked up on this story? If yes, what are they saying about it? No need to lean towards the final conclusion and mindset that all media entitites are false, as this belief on its own is just as inadvisable as following and believing every rumor and conspiracy theory out there.
Examine the evidence
Any credible and trustworthy news story should include plenty of facts that back up the claims and news at hand. This can be through quotes by experts, a survey data and/or official statistics, as well as consistent and corroborated eye-witness accounts from those who were at the scene. Check if if these are missing, and if they are, it would be wise to question them. Does the evidence at hand prove that something happened beyond all doubt? Or have the “facts” been cherry picked and twisted in a particular manner in order to back up a particular narrative?
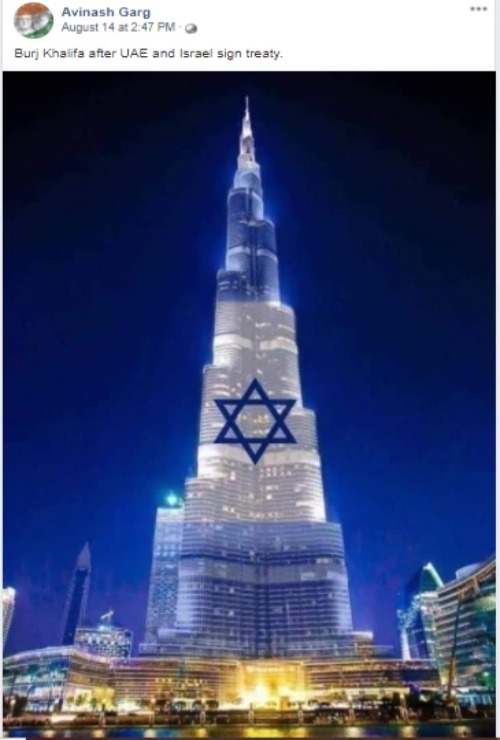

Images taken at face value can be misleading
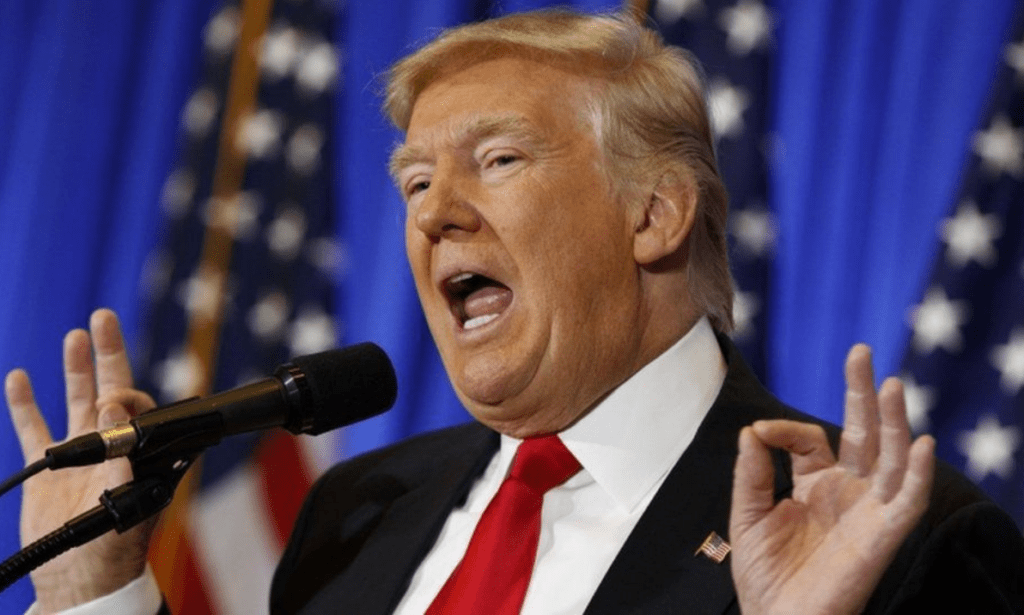
With modern editing software accessible to us today, it has enabled people to create fake images that probably look 100% authentic, such as the one above. Just two days after Israel and the UAE reached in what was considered to be a historic peace agreement, former US President Donald Trump tweeted on August 13th, 2020 about it, and within two days, the above post went viral, and you can be assured that it was believed at face value. However, here are some warning signs you can look out for. One is the appearance of strange shadows within the image, or jagged edges around a figure. Keep in mind as well that although the actual image may be real, it’s also the context and manner in which it is used that one may be manipulated by. For example, photos of children in Syria that have been killed due to the civil war may have originated from five years ago, but are not linked to the recent alleged event. You can try out Google Reverse Image Search to find out the where an image originated from, as well as whether it has been modified and edited in any way.
Does it sound right to you though?
Fake news is specifically designed in order to feed into your existing biases, hopes, fears, and view on the world. Online hoaxers play around with words and content so as to receive more clicks and revenue from ads. One such man is Paul Horner, who, when asked on why he thinks his material receives a large amount of views, he said “They just keep passing stuff around. Nobody fact-checks anything anymore.”