What Role Does LL-37 Play in Arthritis Research?
Studies suggest neutrophils may be the primary source of the cationic peptide LL-37, commonly known as Cathelicidin. LL-37 is comprised of 37 amino acids.
Protease enzymes in the extracellular environment tear down hCAP18 proteins, resulting in LL-37. LL-37, which has been speculated to have antimicrobial potential, may be resistant to breakdown as it may form agglomerates and lipid bilayers.
Research suggests that peptides like LL-37 may assist the immune system in fighting off and preventing various illnesses. The integrity of the immune system is crucial to cellular function. Immunity aids against various diseases, injuries, and disruptions to regulated activities. Many autoimmune illnesses and immunodeficiency disorders exist.
Immune deficiency might be present at birth or developed as a secondary effect of another illness. The immune system weakens and fails to defend the body under certain illness situations. The immune system gradually declines over time.
Click here to purchase LL-37 for your clinical research.
LL-37 Peptide: Mechanism of Action
Antimicrobial peptides are proteins hypothesized to kill microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and even certain viruses. Research suggests that because of the non-specific interaction between these peptides and their targets, resistant strains of infections cannot evolve. Scientists theorize that LL-37 may be necessary to maintain overall immunity against microorganisms as an essential helical peptide.
Based on the premise that the peptide may interact directly with the bacterial membrane, a peptide model was developed as part of the research. These results purported that the peptide may assemble on the bacterial membrane after it has diffused laterally and interacted with the membrane’s lipids through its electrostatic properties. The peptide is further hypothesized to attach to the bacterial membrane and cause a diffusional change, ultimately killing the bacterium.
Findings imply that pore creation on the membrane by the peptide and significant membrane rupture induced by the peptide and lipid complexes are only two examples of the peptide’s possible interactions with microbial membranes that have been speculated in previous research. Researchers have theorized that LL-37 peptides might cause microbial cell death by disrupting their membranes.

LL-37 Peptide Research
LL-37 Peptide and Inflammation
Objectives: LL-37 peptide-induced inflammation was the primary focus of this study.
This in vitro investigation employed tissue cultures, half left untouched, and the other half had the U1 RNA added. U1 RNA is a non-coding RNA widely distributed across the body and released in response to tissue damage.
A genetic study suggested a striking reaction toward epidermal (skin) inflammation and defensive response in the culture presented with U1 RNA and LL-37 peptide.
This research purported that when LL-37 was given to an injured research model body, it appeared to have triggered a systemic reaction that resulted in inflammation and defensive systems.
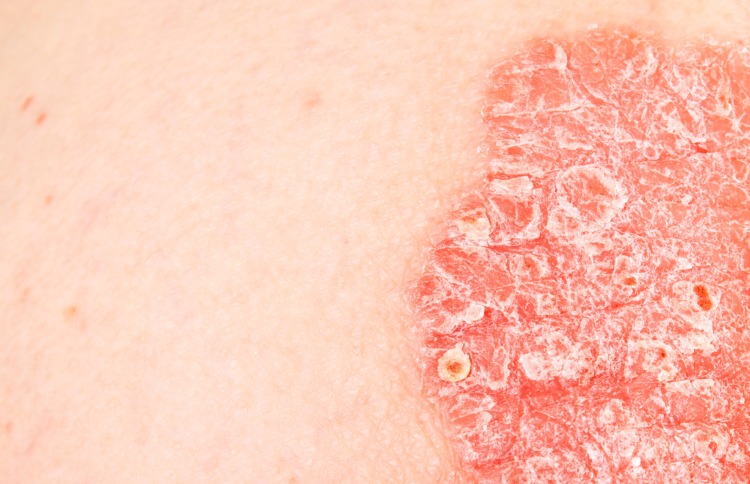
LL-37 Peptide and Psoriasis
The primary objective of this research was to learn if LL-37 may affect the outcome of a Psoriasis diagnosis. Skin inflammation, redness, and itchiness are hallmarks of Psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory skin disease. In this illness state, LL-37 levels are theorized to rise.
Research into disease etiology has uncovered data suggesting that endogenous LL-37 peptide may form a compound with DNA, creating a chain reaction that might result in more interferons and more significant inflammation.
Although this research speculated that higher levels of LL-37 were advantageous for tissue and wound injuries, it is essential to note that excessive LL-37 levels may suggest psoriatic disease. No research has been done to evaluate whether LL-37 could be used as a Psoriasis diagnostic tool.
LL-37 Peptide and Arthritis
Findings imply that research models with rheumatoid arthritis often have abnormally high levels of LL-37. These experiments aimed to determine how essential LL-37 may be in this illness.
In this investigation, rats were utilized, half of which served as a control group and the other half of which had rheumatoid arthritis artificially produced in them. When researchers induced this state, inflammatory cells suggested enhanced regulation of rCRAMP, the rat homolog of the LL-37 peptide. Findings implied that bone resorption seemed to occur due to LL-37’s induction of apoptosis of osteoblasts (cells that build new bones).
This research purports that elevated LL-37 levels could be associated with joint pain and arthritis, suggesting that they might be employed as a diagnostic tool.
Other inflammatory illnesses, such as atherosclerosis, have been assumed to have LL-37 upregulation. Arteriosclerosis-inducing cells are characterized by activation of LL-37 and subsequent overexpression of interferons. This data suggests that LL-37 may be involved in many autoimmune inflammatory illnesses and may be helpful as a diagnostic tool and an immunomodulatory medication.
WE SAID THIS: Don’t Miss…Celebrating World Diabetes Day: Bittersweet…A Brand Offering Products To Help Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetics
