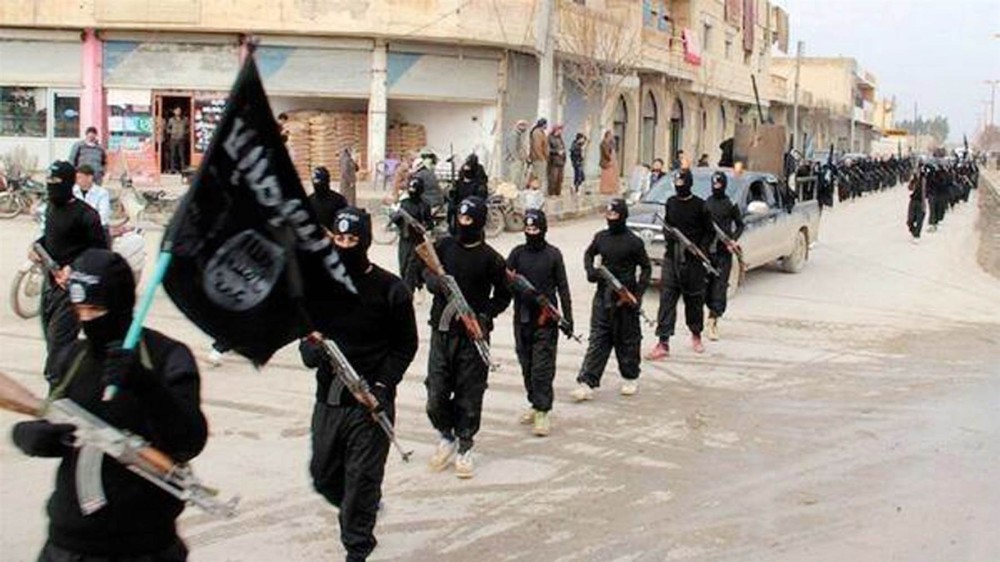
As ISIS continues to grab headlines for barbaric act after barbaric act, we felt we owed you a quick rundown on who they are. Below is our best attempt at making sense of where the group came from, how it sustains itself and what threat it poses to the world.
Where we stand today
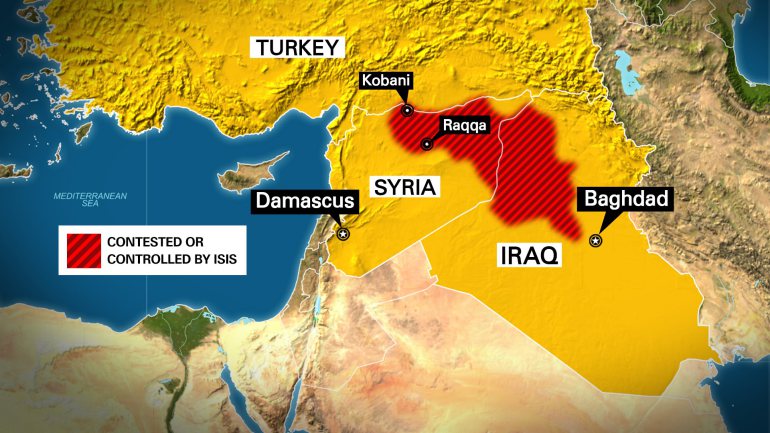
ISIS considers itself the “Islamic Caliphate” (a theological empire) and currently controls vast swathes of land in Western Iraq and Eastern Syria. They also have “allegiance” from different radical Islamic groups around the world (from Afghanistan to Nigeria) who “govern” self-proclaimed provinces.
Within the areas they control, they have established a reign of terror second to none. They have institutionalized slavery and rape (particularly of adherents to the Yazidi religion who they view as devil worshipers) and have carried out genocide and ethnic cleansing of Christians, Alawites and other Shiites and Yazidis among the territories they control.
They have struck with a vengeance beyond their territories. Suicide attacks in Baghdad, Beirut and Ankara killed hundreds. In October 2015, they detonated a bomb aboard a Russian airliner leaving from Sharm El Sheikh airport in Egypt, killing all 224 people on board. In November, they orchestrated a multi-suicide attack in Paris killing 129 people. They have inspired “lone-wolf” terror attacks by sympathizers in places as far away as Ottawa and Sydney.
First, a little bit of nomenclature
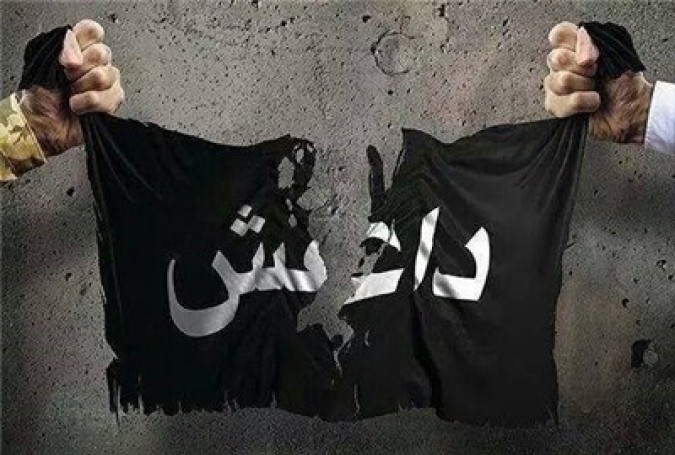

You may have heard about ISIS referred to as IS, ISIL or Daesh. All of these acronyms describe the group in question.
ISIS: Islamic State of Iraq and Syria was the name of the group when it captured Mosul in 2014 and became the terrorist juggernaut it is today. They named themselves that to assert their dominance in Syria (more on that later).
ISIL: Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (aka Greater Syria) is the name that Obama uses to describe the group (only Obama uses it). Superficially speaking, it is just a translation thing.
IS: Islamic State is the name the group gave itself after a “rebranding” effort when they wanted to show off their global strategy (they wouldn’t be limited to Syria and Iraq anymore).
Daesh: You may have heard French President Francois Hollande refer to the group by this name. This is essentially the Arabic acronym of the group. People assume that using this word somehow weakens them… it doesn’t because unfortunately in this case it is one of those “sticks and stones” thing.
Where did they come from?

ISIS was born out of the US invasion of Iraq in 2003. When US administrators, under Paul Bremmer, decided to “de-Baathify” the Iraqi civil and military services, hundreds of thousands of Sunnis formerly loyal to Saddam Hussein were left without a job and very very pissed off. Al Qaeda at the time chose to capitalize on their anger and established Al Qaeda in Iraq (AQI) to wage an insurgency against US troops in Iraq (Saddam was secular, but his intelligence and military supporters were able to make common cause with the Jihadis of Al-Qaeda).
During this time, they were quite active in waging a sectarian war against Iran-backed Shiite militias in central Iraq and bombing hotels in neighboring Jordan. Many of their members were imprisoned in US run “Camp Bucca” where they were able to meet up and get radicalized (think LinkedIn for Jihadis).
Fast forward again to the Arab Spring and the uprising against Syrian dictator Bashar Al Assad (more info on that here). During the Iraq War, AQI would frequently go back and forth between Syria and Iraq to resupply so it had a lot of contacts in the country. When Assad began shooting and gassing his own people and the peaceful uprising turned into a civil war, AQI saw an opportunity to establish a presence there.
It quickly moved into Syria and renamed itself as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and that it was merging with its Syrian counterpart. This pissed off Al Qaeda’s HQ, because they were already establishing a separate Al Qaeda in Syria (aka al-Nusra front) and wanted it to remain separate — terror organizations can be awfully bureaucratic. The two groups fought another mini-war among themselves and officially separated with AQI re-branding itself into the ISIS we hear about today.
It is important to note that this tiff between the two groups was global and concerned some “practical” things (like if Al Qaeda should rule territory or kill Sunnis), as well as ego matters (like if Osama Bin Laden’s lieutenants, who have been on the run since 2001, should be the ones calling the shots). The intra-Jihadi battle was waged on the battlefields of Syria, Iraq, Somalia and North-West Africa, as well as in Jihadi-forums on the darknet (Facebook for terrorists).
As the Syrian Civil War ground on, ISIS became the first rebel group to capture major cities (Raqqa and Deir ez-Zor). In the summer of 2014, the group had its breakout moment. In a lightning offensive, it captured Mosul in Iraq and drove south until it was on the borders of Baghdad. A few weeks later it re-branded itself as a Caliphate and demanded that all Muslims pledge allegiance (bay’ah). At this point groups like Boko Haram in Nigeria and Ansar Beit Al Maqdis in Egypt’s Sinai began pledging allegiance and flew the black flag of ISIS. They also established presences in half a dozen other countries.
ISIS grew in notoriety through an aggressive social media and viral video strategy that had it engage with sympathizers and glorify violence. It beheaded many of its victims, including US journalist James Foley. It often filmed executions through drowning, burning alive and shooting. When it captured the Northern Iraqi town of Sinjar, it institutionalized slavery and rape of the Yazidi minority. In short, it installed a reign of barbaric terror.
But how did they grow to become so powerful?
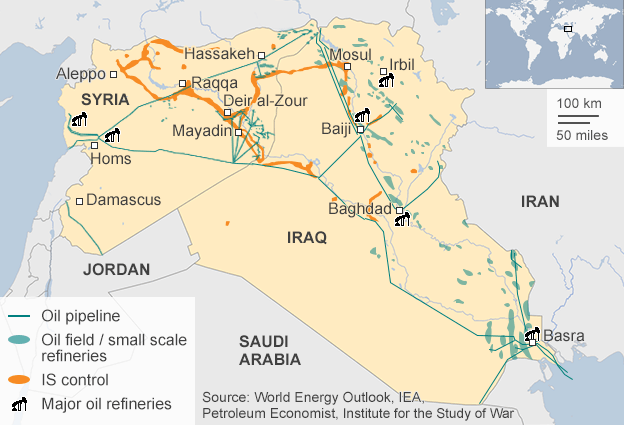
There are a number of forces that can explain how/why it derives its strength. No single one alone is satisfactory (together they might also be lacking).
Feelings of disenfranchisement: Sunni communities in Iraq and Syria felt alienated by Shiite- and Alawite-led governments. ISIS played on these feelings, pushing forward a sense of victimhood and giving these communities a means to feel in control through violence. They also advanced a twisted interpretation of Islam that found ripe fodder among disenfranchised youth in the area.
Unlikely bedfellows: ISIS partnered with the lieutenants of Saddam Hussein’s secular regime (who used to hate Jihadis) to perfect their tools of repression along the same lines that Saddam used.
Syrian chaos: There is little doubt that as US allies (Saudi Arabia, Qatar and Turkey) ploughed money and arms into the Syrian Civil War much of it ended up in the hands of ISIS (and other Jihadi groups).
Iraqi chaos: After the US withdrawal from Iraq, the atrophied Iraqi army was over-equipped and underprepared (and very corrupt) to deal with ISIS. Much of the weaponry ended up in ISIS’s hands.
Racketeering and extortion: Before ISIS formally controlled Mosul, it would run a racketeering business (similar to that used by the US mafia) under the nose of the Iraqi government. Businesses and individuals had to pay them a “protection fee” to stay safe.
Taxation and exploitation: Properties belonging to religious minorities or regime sympathizers were promptly appropriated (e.g. churches, gold, hard currency) and once ISIS controlled territory and people, it began taxing them like any state would.
Selling oil: It is the Middle East, so oil is always involved. While technically shut out from the international markets, ISIS could and did still find markets for its oil (usually in neighboring Turkey whose government was sympathetic to many of the Syrian Jihadis).
So what now?

There are about a dozen countries (some of which hate each other, e.g. Iran, Russia, US) fighting ISIS. All of them (except for Iran, Syria and Iraq) are basically doing it by bombing them from the sky. The US has committed a few hundred “advisors” to the fight (and they are most certainly not wearing boots).
Despite a yearlong campaign against ISIS, the group still controls a lot of territory (even capturing new ground like Palmyra in Syria) and has demonstrated that it can strike in the heart of the western world. In case you were wondering, this is considered a failure of a policy.
Post-Paris, there seems to be growing momentum for ground troop involvement against ISIS. The Obama administration has remained reluctant, insisting that its strategy is the successful one (it isn’t) and that ISIS is weaker now than before (it isn’t). Syrian President Bashar Al Assad feels emboldened with Russia and Iran by his side, knowing that it is less likely for the West to oust him if the alternative will be ISIS.
As the Syrian Civil War closes its fifth year, ISIS seems stronger than ever and the refugee exodus does not look like it will end. As Western governments try to grapple with the threat of ISIS terror reaching the western world, they will feel the pressure to lock out these refugees (who are also fleeing ISIS). By using refugees as a convenient scapegoat, the risk is alienating them, leaving them susceptible to the toxic mix of conspiracy theories and extremism that breeds Jihadi violence.
Note: It should go without saying that while ISIS is a radical Islamic group/movement, it does not, by any means, represent the views of the vast majority of Muslims. The majority of its victims have been Muslims and its twisted interpretation of the Koran is not shared by the one billion+ adherents of the Muslim faith.
Further reading and supporting sources
“The Rise of Islamic State” by Patrick Cockburn
“ISIS: The State of Terror” by Jessica Stern and J.M. Berger
“The Islamic State” documentary by VICE News
“ISIS Enshrines a Theology of Rape” via the NYTimes
“Is This the End of Christianity in the Middle East?” via the NYTimes
“What ISIS Really Wants” via The Atlantic
“Secret Files Reveal the Structure of Islamic State” via DerSpiegel International
WE SAID THIS: For more in-depth analysis of world news topics as well as daily updates of top headlines go to dailyput.com.