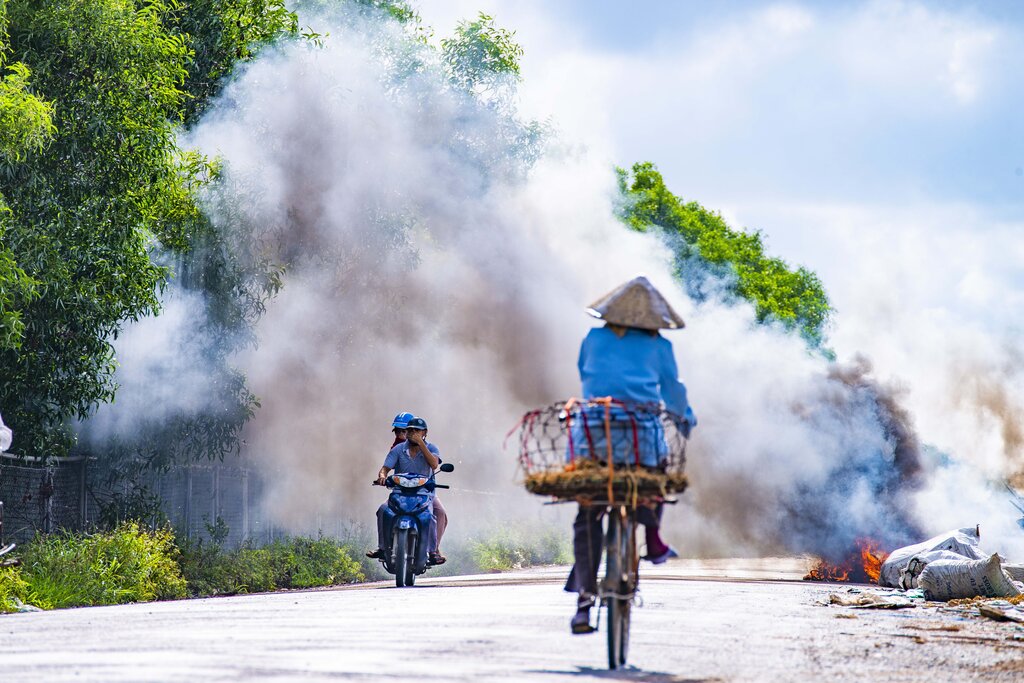
Air pollution continues to be a major environmental issue that needs urgent attention from governments, communities, and individuals. Recent scientific research has shown that air pollution affects billions of people’s quality of life and longevity worldwide. A study by the Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago (EPIC) has revealed that air pollution takes more than two years off global life expectancy. The study analysed satellite data to evaluate the extent of harmful lung-damaging floating particles known as PM2.5.
The Link between Air Pollution and Reduced Life Expectancy
Air pollution is known to cause a wide range of health problems, including respiratory diseases, heart disease, stroke, and cancer. Exposure to high levels of air pollution can also weaken the immune system and compound the effects of other health risks. The EPIC study found that reducing global PM2.5 levels to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recommended limit of 5µg/m3 could increase average life expectancy by 2.2 years.
Fine particulate matter pollution can penetrate the human lungs and even cross into the bloodstream. It is associated with a wide range of health problems, including respiratory infections, lung cancer, and cardiovascular disease. Studies have shown that PM2.5 pollution is more harmful than larger particulate matter because it can travel deep into the lung tissue.
India accounts for approximately 44% of the global increase in air pollution since 2013. On the other hand, if China met the air quality standards set by WHO, its residents could live 2.6 years longer on average. It is worth noting that China has made progress in improving air quality over the past few years, with a two-year increase in life expectancy since 2013 when the country initiated its “war on pollution,” resulting in a 40% reduction in PM2.5 levels.
Environmental Causes
Human activities are the primary cause of air pollution. Burning fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and gas, is the leading cause of global air pollution. Factories, power plants, and diesel emissions from transportation also contribute significantly to air pollution. In addition, agricultural practices, such as burning crop residues and using nitrogen fertilisers, can also impact air quality.
Natural events such as dust storms and wildfires can also contribute to air pollution. However, most air pollution is due to human activities and can be controlled through policy and regulation.
Air Pollution’s Economic Cost
Air pollution has significant economic costs. These include healthcare costs, lost productivity, and the cost of premature deaths. In addition, air pollution can impact tourism, agriculture, and other industries. A Lancet Commission on Pollution and Health report estimates that air pollution costs the global economy $4.6 trillion yearly, equivalent to 6.2% of global GDP.
Environmental Activism for Change
The air pollution problem has prompted many environmental activists and agencies to act against this problem. One strategy that many countries have embraced is adopting stricter laws on emissions from cars and factories and incentivising the production of renewable energy sources. Additionally, there has been a growing trend of developing public awareness campaigns and policies to mitigate the effects of pollution in urban areas.
The Volkswagen emissions scandal, known as Dieselgate, highlighted the rise in diesel emissions and the need for stricter regulations in the automotive industry. The scandal involved the discovery that Volkswagen had installed defeat devices in its diesel vehicles to cheat emissions tests, resulting in significantly higher emissions than the cars were supposed to produce.
Countries like Sweden and Denmark have made significant strides in mitigating the impacts of air pollution. For instance, Stockholm transformed its public transportation system to renewable energy, reducing emissions from cars by 49%. On the other hand, Denmark has implemented aggressive measures to reduce the use of motor vehicles and promote green transportation to combat carbon emissions.
The Importance of Individual Actions
While governments and organisations significantly improve air quality, individuals can also reduce air pollution and improve air quality. These include:
- Opt for eco-friendly transportation: public transit, cycling, or walking instead of relying solely on driving.
- Supporting businesses that prioritise sustainable practices and use renewable energy sources.
- Reducing energy consumption, such as turning off lights and unplugging electronics when not in use.
- Reducing waste, recycling, and using reusable products wherever possible.
- Being informed and engaged in environmental policy and advocacy.
- Protecting their rights as consumers by filing a diesel emissions claim at Claimexperts.co.uk.
Bottom Line
Air pollution has been a pressing issue for many years, but the latest study’s findings present compelling evidence of the scale of the problem’s impact on public health. Two years off global life expectancy is a devastating consequence that must be taken seriously by policymakers and industry leaders alike. The diesel emissions scandals, notably Dieselgate, have shown the link between diesel emissions and the harmful effects of air pollution. It highlights the importance of regulation, transparency, and accountability in ensuring vehicles’ compliance with environmental standards.