By Sherif Awad
In 1980, American physicist Paul Benioff, set the first milestone for developing a new kind of computer (quantum computer), that far more powerful than our normal computers. He demonstrated the theoretical possibility of quantum computers.
What is quantum computing?
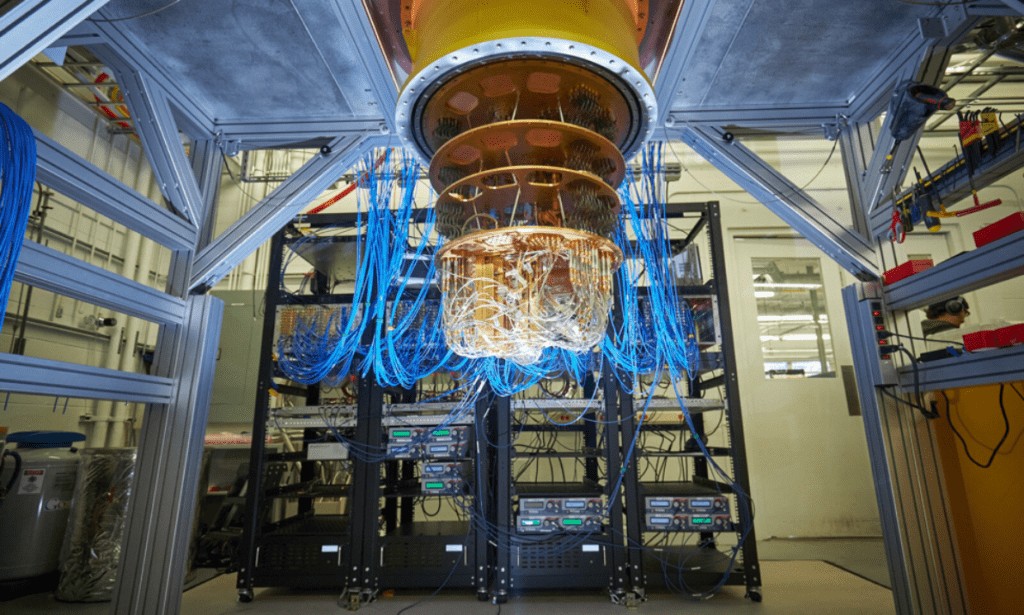
Quantum computers are based on quantum mechanics, and they can perform computations much faster than normal computers. They can solve complex problems that the fastest super computer cannot solve. A quantum computer can solve a problem that takes one week on a normal computer in one second, or in some other scenarios, a real quantum computer solved a problem that would take the world’s fastest computer 10,000 years in 200 seconds. Quantum computers can be used to solve the most complex problems from finance, security, to cancer research. Scientists expect to have real use of quantum computers by end of next year, full applications by 2026, and commercial use by 2030. To reach commercial scale quantum computers, it is going to require revolutionary discoveries in physics, material science, computer science, and mathematics.
What is the quantum security (post-quantum cryptography)?
The communication on the internet is protected by cryptography. Cryptography protects our information, as it travels over and is stored on the internet. Quantum computers are so powerful, they can break into the world’s most complex cryptography in seconds, and that poses a threat to the world. It can break into governments, enterprises, or global organization systems. IT organizations around the world are working on creating new cryptography methods that cannot be broken by quantum computers. The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), is working on standardizing cryptography algorithms that cannot be broken by quantum computers.

What is the quantum race and who is winning?
Quantum computers exist today, but they are not as powerful as we need them to be in order to solve the most complex problems that we have today. Quantum computers’ speed can be measured in qubits, which is the basic unit of quantum information like bits in normal computers. IT giants are battling for quantum supremacy such as IBM, Google, Microsoft etc. Google claimed quantum supremacy in 2019 by building a quantum computer with 53 qubits. A team of Chinese scientists in 2020 have developed the most powerful super computer that is able to perform a single task 100 trillion times faster than the world’s fastest super computer. China has invested $10 billion on the country’s National Laboratory for Quantum Information Sciences. That does not mean they reached quantum supremacy, as their computer is specialized in doing a single task really fast, unlike the Google general quantum computer.
How does it affect the Middle East?
Any security that we have today will be useless by 2030. That means that the IT systems that we rely on today such as electricity, networks, hospitals and supply chains, could be down in seconds. Governments, enterprises and global organizations need to change their security systems to be post-quantum proof, which means they will invest heavily in new security agile systems that can adapt to new security protocols as they arise.
Congress passed the National Quantum Initiative Act which requires presidents to be advised about the developments in the field, and the World Economic Forum has advised that we need to build quantum literacy program in governments.
Do we need to have quantum security today?
Imagine that some encrypted secure data got stolen from you today. In a few years, quantum computers will be able to decrypt the data that was stolen. If your data becomes irrelevant in five years, then you shouldn’t care about it being decrypted in five years. But, if it is government data, then defiantly you need to start thinking about quantum security today.