Arabic Calligraphy, the art of creating decorative handwriting or lettering, is one of the oldest art forms from the Arab region; one that has not only thrived with time but also evolved into a unique form of expression. It survived through several tumultuous periods that threatened its existence, from civil wars to an invasion by the Mongol Empire that destroyed Baghdad.
Even though the writing wasn’t as focused on in the past, with many Arabs preferring to memorize poetry and other forms of text and pass them down verbally, that changed significantly later. Calligraphy would flourish to include the preservation of the Quran, adorn mosques as well as the palaces of kings, and by royal scribes when writing decrees, among other things.
In celebration of World Calligraphy Day, we decided to dive into the past and look back at some of the most well-known and prominent calligraphers from the Arab world.
Ibn Muqla
One of the biggest names in developing and improving Arabic calligraphy, born in 885 AD in Baghdad, Iraq, during the Abbasid Caliphate, he started out as a tax collector before rising through the ranks and becoming the Caliph’s Vizier three different times.
At this time, the Kufi style dominated the calligraphy scene, but Ibn Muqla invented new art styles that superseded the previous ones. Ibn Muqla was the one who invented the Thuluth and Al-Mansoub styles, as well as the foundations and rules for others, such as Naskh. The Naskh and Thuluth got further development throughout the centuries that followed, and calligraphers still use them today.
While the Kufic style was rigid in its overall design, Naskh had a more cursive structure but wasn’t as popular and as used at the time, Ibn Muqla changed that by improving on it and using it in official decrees, and private correspondence.
Ibn Muqla’s Thuluth style was new with its letters having long vertical lines with broad spacing. Its name translates to “one-third”, in reference to the maximum height for the letters on the same line must not exceed one-third of the ‘alif.
As for the Al-Mansoub style, it mainly focused on three measurements: the size of the period meaning the “Noqta”, the circle with a diameter equal to the height of the alif (the first letter in the Arabic language) and, and the height of the alif.

Ibn Al-Bawwab
Little is known when exactly Ibn Al-Bawwab was born. However, we know of his existence and his body of work thanks to the survival of many of his manuscripts, Qurans, and texts referring to him by name.
With his name literally translating to “son of the doorman,” he didn’t grow up in a wealthy family and had to work to make a name for himself. He did so by learning about law and theology and working in several professions, such as a home decorator. However, he would later settle on working in book illumination and calligraphy.
Over years of hard work, he became renowned as a master calligrapher; fluent in six different styles in the field, perfecting the Al-Mansoub style and developing the Reyhani, Naskh, Tawqi, and Muhaqaq styles significantly.
Housed at the Chester Beatty Library in Dublin, Ireland, is the sole surviving Qur’an penned by Ibn al-Bawwab gifted to the country by Ottoman Sultan Selim I.

Mohammad Hosni
Originally from Syria, Mohammad Hosni Al-Baba was born in 1894 and is considered one of the last classical calligraphers. Al-Baba received his initial formal training with the Turkish master, Istanbul-based Yousef Rasa, who had renovated the Umayyad Mosque in Damascus, Syria. Al-Baba would later study under another renowned calligrapher, Mehmed Showki Afendi, author of the work “The Thuluth & Naskh Mashqs.”
He would later travel to Cairo, Egypt, becoming one of the leaders in Islamic and Arabic calligraphy, turning his home into a hub for artists, calligraphers, and poets. Al-Baba would be famous for improvements to the lettering in the Thuluth style, the linear structure of Arabic script, and was appointed by King Farouk as the first professor to be a master at the Royal Institute of Calligraphy.
His children would continue his legacy but in different fields since many grew up surrounded by artists when they visited Al-Baba’s home. The most famous of his children are actress Soad Hosni, dubbed “Cinderella of Egyptian Cinema,” and Najat Al Saghira, who became an actress and singer.

Hassan Massoudy
Born in 1944, Iraqi painter and calligrapher Hassan Massoudy continues to be one of the biggest inspirations for many modern artists today. French writer Michel Tournier even considered him as the “greatest living calligrapher” in 1989.
Massoudy grew up in Baghdad, Iraq, until 1969, when he fled to Paris, France, entering the École des Beaux-Arts, where he studied figurative painting. At the time, he looked for a job to pay for his studying, finally finding one as a calligrapher in Arabic magazines, writing their headlines.
While he wasn’t famous for a traditional calligraphy style, his distinct and elaborate designs made him stand out among the rest of the artists of his time. Massoudy would delve into the world of theater, collaborating with artists and choreographers, creating different productions focusing on the harmony of dance, calligraphy, and dance routines.
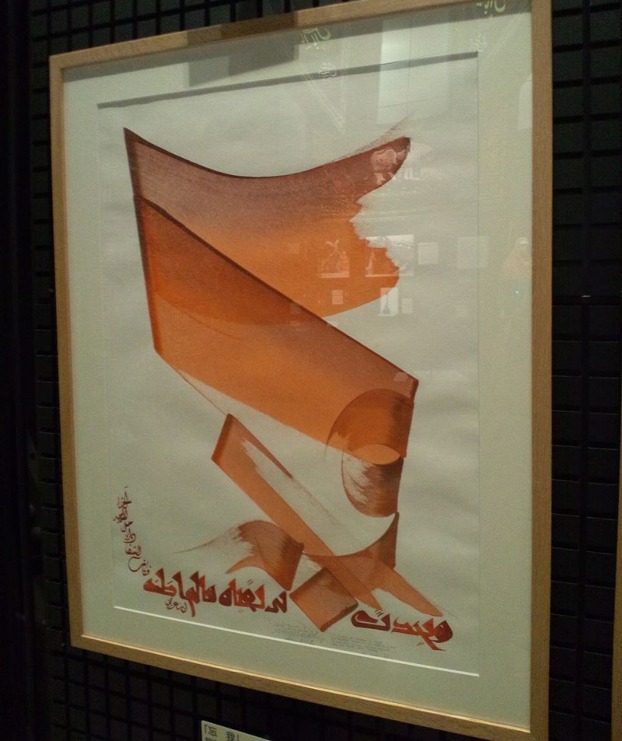

Nja Mahdaoui
Studying abroad but seeking inspiration from his traditional roots, Tunisian artist and calligrapher Nja Mahdaoui invented the world of Arabic calligraphy as a graphic style, creating what was called “Calligrams.”
Born in 1937 in Tunis, Tunisia, he first started learning art history and painting at the Carthage National Museum. He later traveled to Rome, Italy, where he continued to study painting and learned more about philosophy at the Santa Andrea Academy. He also moved to Paris, France, where he went to the Cité Internationale des Arts and École du Louvre before returning to his home country in 1977.
His calligraphic style focuses mainly on the designs he creates as a whole rather than the composition of words since his “calligrams” resemble Arabic letters but have no literal meaning, leading to many naming him the “inventor of abstract calligraphy.” People can see Mahadaoui’s work on several materials used as a canvas, including jewelry, drums, leather, paintings, walls, glass, and so much more.
A UNESCO Crafts Prize laureate, Mahdaoui, graced the Facebook campus in 2018 by painting one of their halls using Arabic calligraphy in his unique style as part of the “FB AIR program,” turning their hall into a vividly colorful masterpiece.
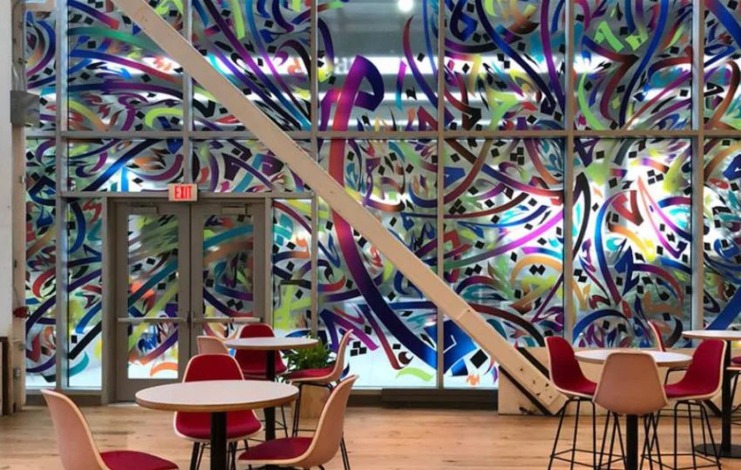

Ahmed Mustafa
Egyptian artist and calligrapher Ahmed Mustafa was born in 1943 in Alexandria, Egypt, graduating from the Faculty of Fine Arts at Alexandria University in 1966 before traveling to the UK on a scholarship to the Central School of Art and Design in London, England, where he earned his Ph.D. in 1989.
Inspired by his Islamic roots, his calligraphic works mainly focused on quotes from the Quran, among other sources. Working on several materials as his canvas, Mustafa has designs on glass and carpets, among others.
Mustafa also set up the Fe-Noon Ahmed Moustafa Research Centre for Arab Art and Design in London in 1983. He lectures and creates workshops globally as well as does commissions, one of which was presented by Queen Elizabeth II to Pakistan for the country’s fiftieth anniversary in 1997.
The following year, the Vatican invited him to do an exhibition at the Pontifical Gregorian University in Rome, Italy. World media at the time announced it as the first achievement of its kind in the history of Muslim-Christian relations.

We Said This: Don’t Forget… Exhibition Based On Prophet Mohamed’s Hijrah Awes Viewers