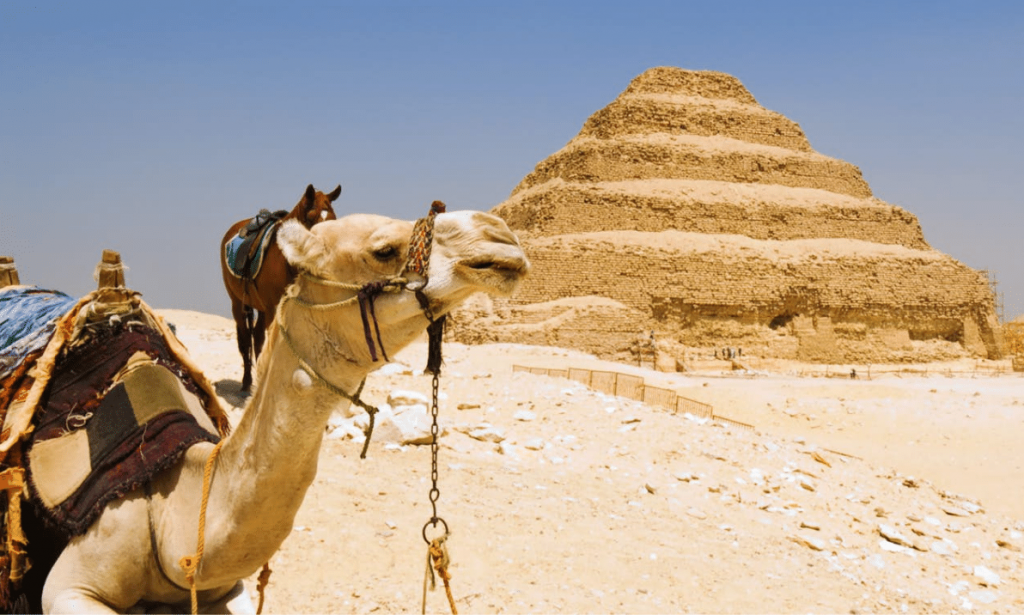
Although Egypt has more than one-third of the world’s historical monuments, many people aren’t aware of the gem that Saqqara is. Saqqara is home to Egypt’s oldest pyramid, the Pyramid of Djoser, and the nation’s largest archaeological site. The Pyramid of Djoser is also the world’s oldest surviving stone building.
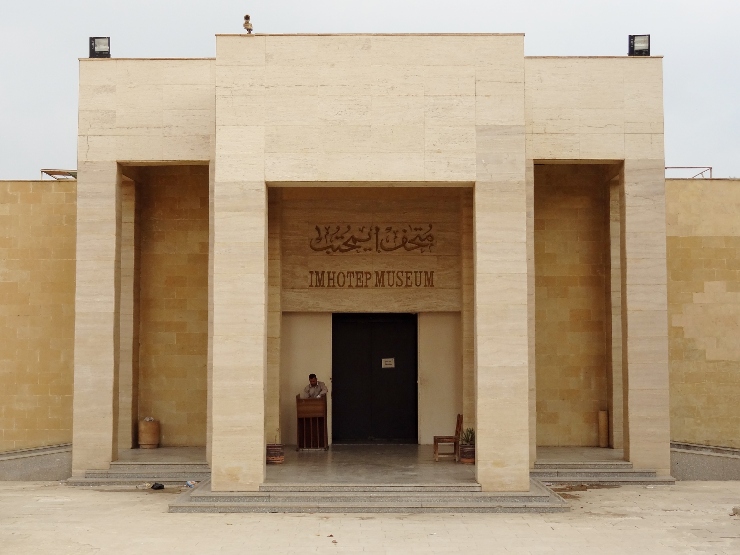
Adding to the wonder of the pyramids, Saqqara also houses Imhotep Museum, which was named after the former Egyptian architect Imhotep, who is credited with the construction of Egypt’s first pyramid.

Located 40 km southwest of Cairo, Saqqara, which is a designated UNESCO World Heritage Site, was one of the most important cities in ancient Egypt. Saqqara was Egypt’s first capital, and is mostly famous for including the tombs of Egyptian kings, dating back to the first and second dynasties. It later became the royal burial ground for the fifth and sixth dynasties as well.
With 11 pyramids in total, up until today archaeologists are still making superb discoveries in Saqqara, through ongoing excavations and digging. Recently, Egypt’s Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities announced the discovery of 14 fully-intact sealed human coffins, following last week’s discovery of 13 others, bringing the total to 27 sarcophagi buried more than 2,500 years ago.