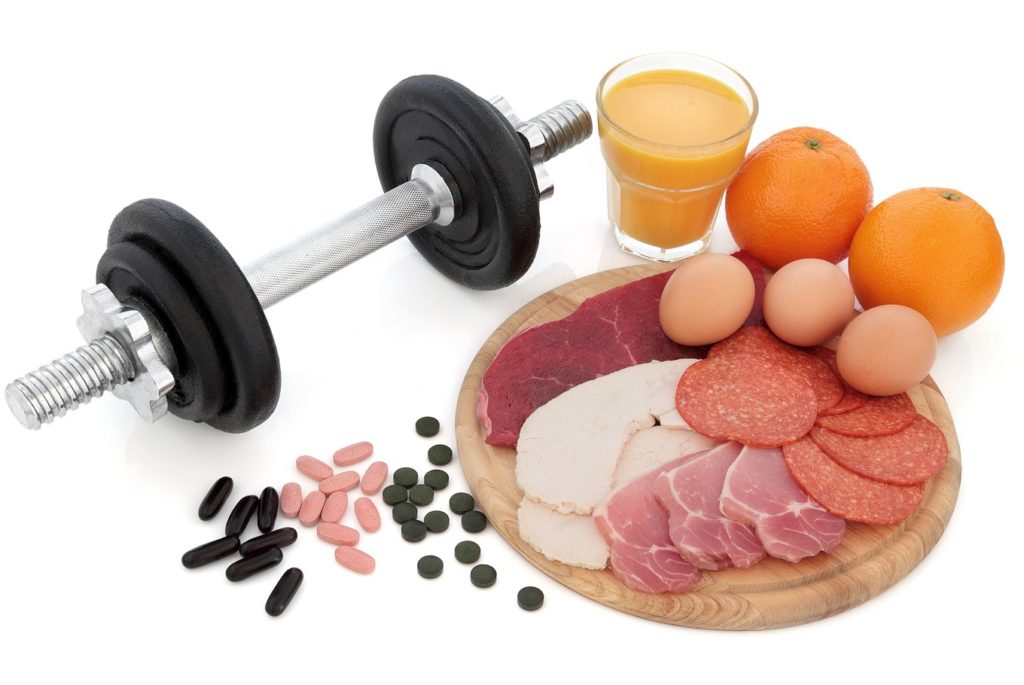
Would you like to become enormous? All you have to do is go to the gym, pound out reps, come home, and resume your normal routine, right? If only bodybuilding was really that easy. Nutrition is crucial to recovery, development, and overall fitness; without it, your body will not gain lean muscle mass. If you really want to be a bodybuilder, you’ll have to adjust your lifestyle and adopt a muscle-building diet. Don’t worry, it’s not as difficult as it seems. We’ll show you how to assess your nutritional requirements and bodybuilding meal prep ideas in order to develop a muscular physique.

What is the Concept of a Bodybuilding Diet?
Most people who exercise for athletics, bodybuilding, weightlifting competitions, or to boost their level of fitness are attracted to a bodybuilding diet to gain muscle and achieve a lower body fat percentage.
A traditional bodybuilding diet consists of increasing total protein and calorie consumption while still including daily aerobic exercise in your workouts. Based on whether the target is to just get stronger, increase muscle mass, or train for competition, the program suggests steadily raising weight, intensity, and repetition.
Dietary habits for weight lifting and bodybuilding are not dissimilar from a healthy, well-balanced diet rich in nutrient-dense items. The focus on the amount and meal scheduling during different phases of weight training is the exception with a bodybuilding diet. Many endorsers of a bodybuilding diet use dietary supplements to gain strength. However, nutrition experts suggest getting your nutrition from actual, fresh foods whenever possible. Learn about the benefits and drawbacks of a bodybuilding diet to see if it’s a good way to achieve your strength and conditioning goals.
Five Pillars of Nutrition
Protein that is low in fat: To accelerate muscle development while also triggering the release of fat-burning hormones, provide your body a protein infusion every couple of hours. Lean beef, fish, chicken, lower-fat dairy foods, and soy are great options. Although whole grains should be your first preference, a high-quality protein powder will help you reach your protein requirements daily. Consider supplementing with a whey protein shake between other meals, and use slow-digesting casein protein for fueling your gains when you sleep.
Carbs in a strategic sequence: Carbohydrates are divided into two types: starchy, fast-acting carbs like bread, rice, and pasta, which increase blood sugar rapidly, and non-starchy carbs like vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, that are rich in fiber and lift blood sugar slowly. Carbohydrates that aren’t starchy are rarely a concern. Have fun with them! When it comes to having and keeping a lean as well as muscular body, the scheduling of when you ingest starchy carbs is crucial. Your body is more willing to use them to restore your energy reserves if you have them first thing in the morning or right after your workouts.
Keep yourself hydrated: Keep your workout performance at its best by drinking water and calorie-free drinks. Avoid sugary drinks, which can add inches to your waistline and weaken your body’s antioxidant defenses.
Six meals a day: To maintain your level of blood sugar under control, your metabolism stable, and promote the development of new muscle, help your body with several smaller meals and snacks throughout the day.
Limit processed foods: Anything with a logo or a brand name, whether in a package, a carton, or a bag, is possibly heavily processed and not good to eat. You’ll be much more sufficient to make your New Year’s goals if you eliminate these nutrient-poor, high-calorie foods from your diet.

Phases of bulking and cutting
The bulking phase and the cutting phase are the two main stages of a bodybuilding diet. Bodybuilders eat to gain muscle and lose weight in preparation for competition, burning the fat away and leaving the muscle to reveal. It’s known as “cutting.”
Followers usually increase their calorie consumption by around 15% during the building process. However, during the cutting process, energy consumption is reduced by the 15% that’s been added, and the diet must be somewhat low in fat, about 20%. It’s suggested that you consume about 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight (2.2 grams/kilogram) during either phase.
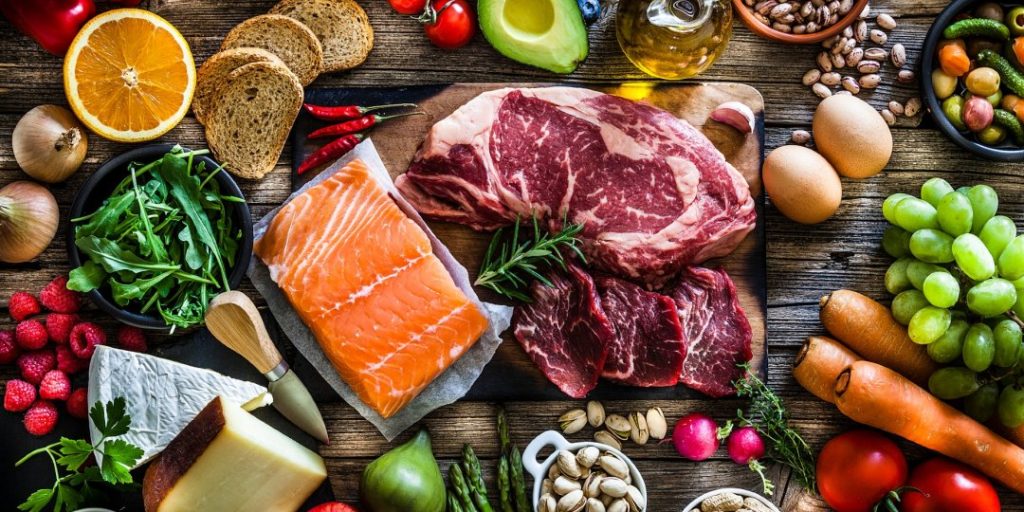

Grocery List
To support energy and muscle development, eat mostly starchy carbs and fewer fats before and after sessions. You’ll consume like this more often if you’re trying to gain weight. You must restrict starches after a workout, keeping you on track to achieve your fat-loss targets. Your meal choices for foods that contain starchy carbohydrates include:
- Brown rice, potatoes, oats, quinoa, yams, whole-wheat pasta, pizza, cereals, and wraps are all good sources of starch.
- Protein powders, white meat, white fish, egg whites, whole eggs (in moderation), and Greek yogurt are all good sources of protein.
- Green/fibrous vegetables, tropical fruits, and beans are examples of vegetables, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Use just a few teaspoons of oil, not tablespoons.
You have the following choices for meals that do not have starchy carbohydrates:
- Protein powders, white meat, red meat, eggs, fatty fish or white fish, and Greek yogurt are all good sources of protein.
- Berries, green/fibrous, and beans are examples of fruits/vegetables/legumes.
- Tablespoons, not teaspoons, for oils and fats. Avocados, nuts and seeds, canola mayonnaise, coconut oil, and full-fat cheeses are all good choices.
We want to conclude that there is no such thing as a one-size-fits-all solution to living a healthier lifestyle. Individualized diet plans that recognize the individual circumstances are necessary for success. Meet your primary care physician or a registered dietitian before beginning a new diet plan, particularly if you have any underlying health condition.