For the majority of seniors, maintaining health is the key to living a long and fruitful life. This can be especially true for those suffering from diabetes. Experts tell us that seniors with diabetes are more likely to develop other health complications than other older adults without diabetes. So, whether you’re approaching your golden years or have already achieved them, it is important to know how to manage diabetes in your golden years.
With the overwhelming increase in the elderly population and thus, the increased cases of diabetes, it is no secret that diabetes is fast becoming a significant health problem faced by senior citizens. This certainly leads to paying special attention to the concept of managing diabetes.
The fact that the number of people with diabetes is increasing is well-known. However, what is not so well-known is that this increase is particularly high among people over 65 years of age. This means that the number of seniors with type 2 diabetes will continue to grow at a fast pace. The good news is that many older adults can manage their disease successfully.

Are Older Adults More Likely to Develop Type 2 Diabetes?
It is indeed true that older adults are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than younger people. Well, there are several reasons why older adults are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than younger people:
They may have had diabetes for a longer time and have more complications from it than younger people; they may also be taking medications that affect their blood glucose (BG) levels or cause weight gain and obesity, both risk factors for developing diabetes; they may have less muscle mass, so insulin resistance develops more quickly, and they often have other risk factors such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels that increase the chances of developing diabetes.
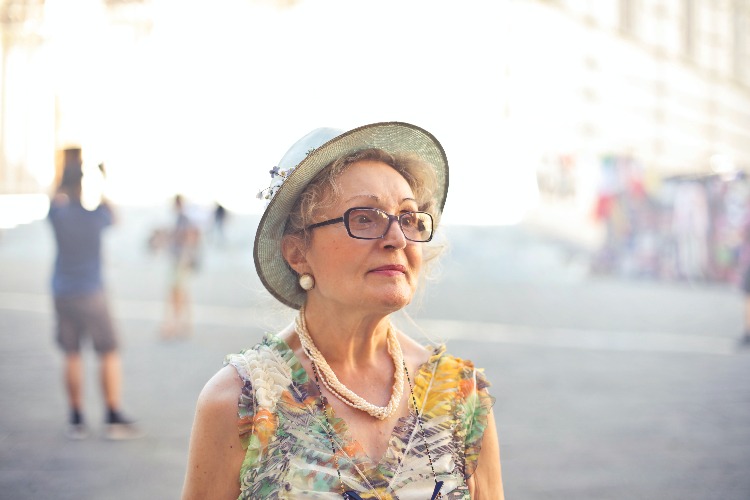

Tips for Managing Diabetes in Your Golden Years
The prevalence of diabetes is rising among older Americans. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than one in four adults aged 65 years or older has diabetes, which increases their risk for serious health complications.
The good news is that managing diabetes in your golden years, i.e., in your senior years, it doesn’t have to be difficult if you’re proactive about it. Here are some guidelines that can help you with managing diabetes:
Pay attention to what you eat: The food you eat plays an important role in managing diabetes by keeping an eye on your blood sugar levels and preventing complications such as heart disease. Eat a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, and limit your intake of red meat and processed foods.
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise helps control blood sugar levels by burning extra calories and strengthening muscles that help with insulin absorption, and hence, helps in managing diabetes. Experts recommend at least 30 minutes of aerobic activity five days a week for optimal results. You should also do strength training twice or thrice a week for additional health benefits.
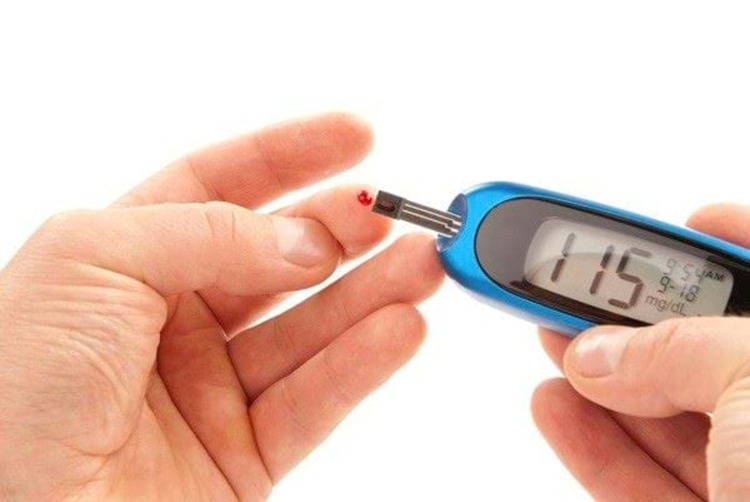
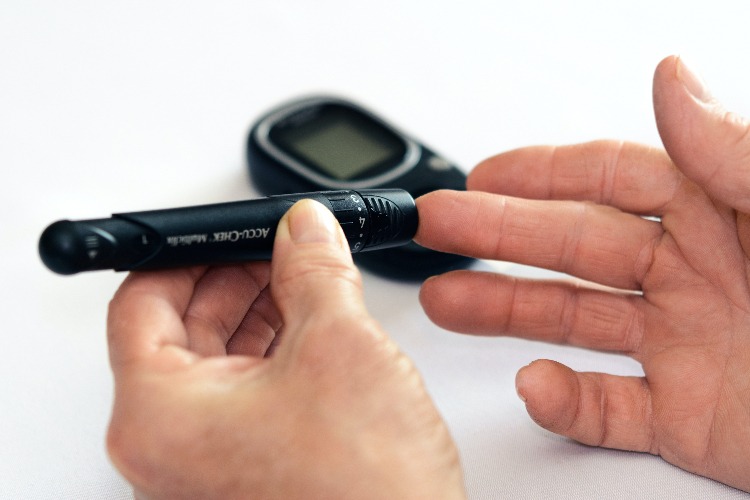
Monitor your condition regularly: You should monitor your blood sugar levels at least three times daily — before breakfast, after lunch, and before dinner — using a glucometer kit or meter. Make sure to test yourself after meals because this will give you an idea of your daily blood sugar level.
Manage stress: Use stress management techniques such as meditation and relaxation therapy for managing diabetes. The more stress you feel, the more it is going to affect your health.
Diabetes is a chronic disease that impacts the way your body uses sugar. It occurs when your pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin or when your body’s cells don’t respond to insulin properly. Insulin is a hormone that enables sugar in your blood to enter your cells and convert it into energy.
Over time, high blood sugar can damage nerves, kidneys, and blood vessels. If you are struggling with managing diabetes, you need to take steps to keep your blood sugar under control.

How Does Diabetes Affect Aging?
As you age, the risk of developing diabetes increases. So does the risk for complications from this condition — including heart disease, nerve damage, and eye disease — due to long years with diabetes. However, if you have type 1 diabetes (which usually develops before age 30) or type 2 diabetes (which develops at any age), there are things you can do to help prevent or delay complications with aging while managing diabetes at the moment:
Maintain good nutrition.
Keep track of weight changes.
Exercise regularly and increase activity gradually as strength allows.
Try to stay hydrated all the time.
The most important thing while managing diabetes is to avoid spikes in blood sugar. It’s also indispensable to monitor your blood pressure, weight, and cholesterol. Two or three times a year, go through a proper medical checkup, screening for potential complications like kidney disease and heart disease. Finally, speak up and tell people around you that you have diabetes if they haven’t figured it out on their own. We’re all getting older – this is the time when we need our loved ones’ support the most.
WE SAID THIS: Don’t miss…Are Your Sleeping Conditions Giving You Health Problems?